
Innovation within an organization is tied to its people. With 78% of companies using some type of ERP consultants, we are already aware of their indispensable role in driving ERP project success. In 2024, more volatility and macroeconomic shifts are destined to reshape the ERP ecosystem and global business world. Therefore, it would be wise to be discerning about the ERP skills that your business may need this year.
Our conversations with ERP consultants and their experiences often highlight the importance of having a proactive approach to planning and strategizing ERP projects. Unfortunately, many organizations react when ERP deployments and implementations fail to meet their expectations. Almost 75% of ERP projects fail, and 44% exceed the actual budget, suggests a Deloitte survey. Even though the project failure risks are high, the average return on investment (ROI) from an ERP project is 52%. This means that every dollar spent on an ERP system can potentially deliver a total return of $1.52. But the payback on ERP software investment takes at least two to three years! It can take much longer without proper guidance and the right ERP skills of experienced professionals.
In our previous blog, we explored the ERP trends for the year. Charting a list of expectations in terms of the types of ERP skills helps simplify the management of complex requirements of ERP systems. We zeroed in on the 12 must-have ERP skills your business can seek from ERP professionals:
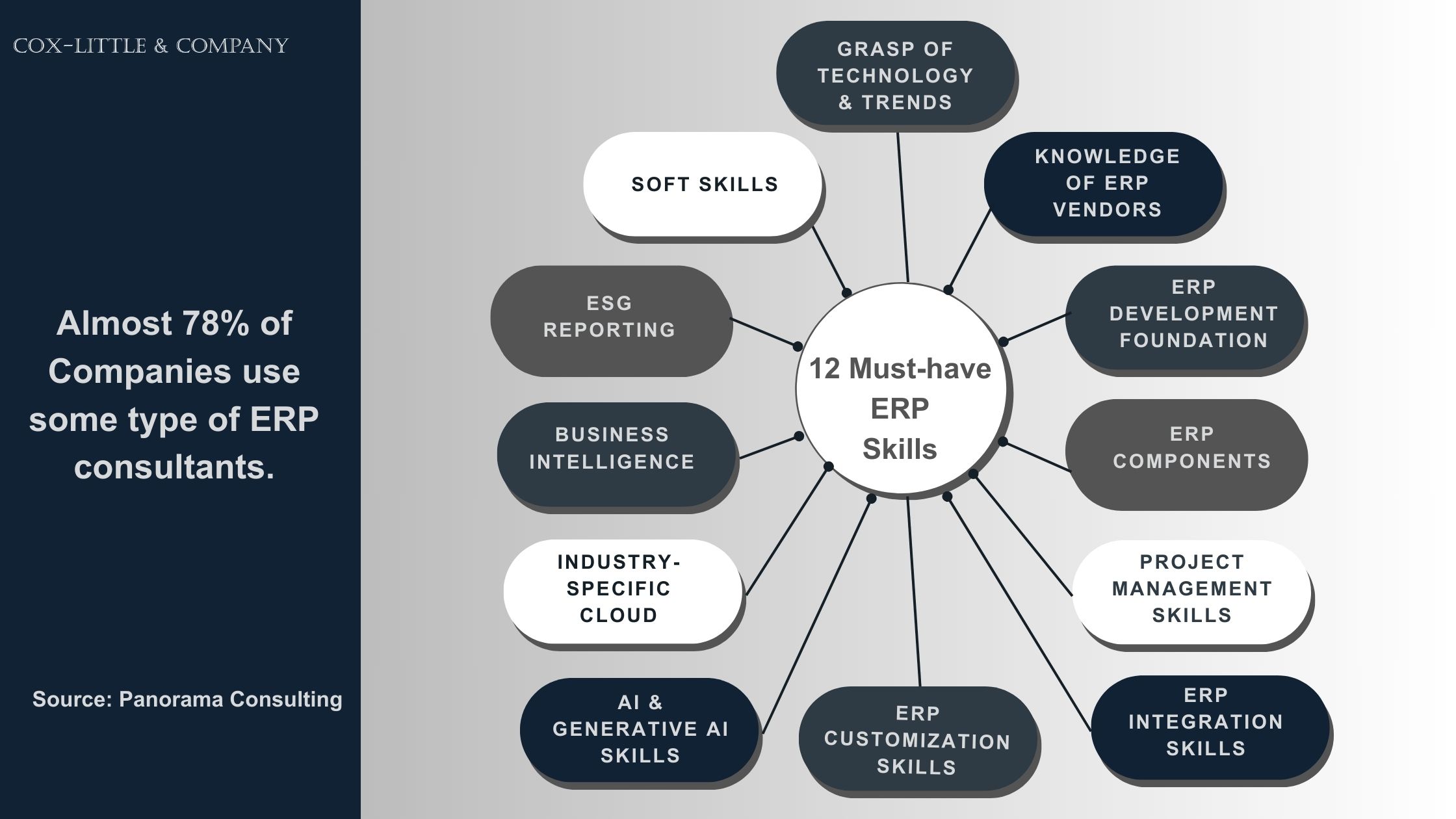
- Grasp of Technology Trends: Understanding the latest technologies and trends broadly impacting the ERP software ecosystem is vital for ERP consultants, developers, administrators, and analysts. According to research by Panorama Consulting, nearly 46% of companies hire ERP professionals to make technology assessments, 51% for organizational change management, and 25% for digital strategy. Businesses need consultants with hands-on experience and knowledge of the tech space to offer insights beyond what their internal tech teams can offer. That may include deep knowledge about the tech architectures, local and standard data processing and protection regulations, and industry-specific functionalities to help firms ace their ERP projects. It is a given that ERP consultants should have a solid awareness of emerging concepts such as AI, GenAI, smart factories, metaverse, predictive analytics, low-code developments, and more.
- ERP Vendor Knowledge: The market is flooded with many large ERP providers such as SAP, Oracle, MS Dynamics, Sage, and Infor, promising a tapestry of pre-configured features and benefits. However, buyers can’t always know the right product fit and may choose ERP software with out-of-the-box functionalities that may not fit well with their enterprise needs. Often, the promises and claims of the ERP providers end up being self-serving. ERP consultants’ expert opinions are required during the vendor evaluation to avoid decision fatigue and wrong product selection. With exclusive vendor certifications and domain-specific skills, ERP professionals in product selection based on functionality, scalability, budget, upgrade cycles, and project scope.
- ERP Development Foundation: ERP systems are multilayer software that contains modules, extensions, blocks, and elements. The front-end and back-end and development technologies (Java, .NET, and Python) and underlying ERP software architectures (microservices and monolith) and IT infrastructure (cloud computing platforms and database) influence the ERP software’s security, scalability, flexibility, usability, and interoperability factors. Dedicated ERP developers who fully grasp your firm’s requirements can execute fundamental decisions such as the best programming language, number of modules, perfect UX, testing, design, and deployment.
- ERP Components: ERP components such as accounting, human resources (HR), supply chain, distribution, and logistics management, risk management, sales order management, customer relationship management (CRM), and financial management are also known as modules. The modules are the building blocks of ERP systems. They are added or removed as needed. Modules can easily be integrated into the centralized ERP system to provide a unified view of the data to save time, collaborate with teams, and improve productivity. An ERP consultant with knowledge of these components can help choose those to enhance business performance and decision-making abilities.
- Project Management Skills: After choosing a relevant ERP provider, firms need a project process checklist to understand intricate requirements for implementation, deployment approach, customization, automation, data migration, processes and systems integrations, change management, and more. ERP consultants help build a comprehensive project plan with realistic timelines, risk management, and task and resource allocations throughout the project lifecycle. Project management helps reduce the scope for errors, redundant workflows, wastages, and manual steps to streamline teams and resources for successful ERP project completion.
- ERP Integration Skills: ERP integration with existing systems and applications using standard APIs is in demand. Additionally, organizations today need the expertise of ERP professionals to leverage integration with AI and ML to unlock predictive analytics and insights and intelligent process automation to boost productivity, reduce manual processes, and enable prompt decisions.
- Hands-on ERP Customization: ERP implementation is not the end goal; organizations must tailor the ERP platform with their existing processes, workflows, and business requirements to fit like a glove. ERP customizations could be minor tweaks to profound modifications that need coding or development to achieve unique features and functionalities that standard ERP features and modules cannot deliver. ERP consultants with enough experience can help decide customization needs based on the available systems and applications, existing workflows, industry-specific features, scalability requirements, IT dependencies, and future upgrades.
- AI and GenAI Skills: Most modern cloud ERP platforms have AI and GenAI capabilities. As ERP vendors continue adding new features powered by these technologies, customers may want to know more about the right AI models to leverage and implement performance enhancements that make their business operations error-free, efficient, and profit-driven. To help know what functions and GenAI features to embed, firms need the help of experts with recent generative large language models and GenAI algorithms to realize the transformative potential of ERP platforms.
- Industry-specific Cloud: Generic ERP platforms need large customization levels to make them more conducive for usage and adoption. Some native ERP features do not apply to all businesses and industries. Industry-specific cloud platforms are increasing exponentially. According to Gartner, 39% of companies have started adopting industry cloud platforms, and by 2027, the number will reach 70%. ERP system users must leverage them to scale their business quickly and improve efficiency and performance. ERP consultants with knowledge of industry-specific editions, data fabrics, and tooling beyond traditional ERP platforms can help firms increase speed, accuracy, and ROI.
- Business Intelligence: ERP systems have business intelligence (BI) features embedded using powerful data analytics capabilities to enhance operations and forecast trends. BI tools native or integrated into ERP systems allow accurate reporting and visualization of data analyses. Firms need an experienced ERP professional to understand robust BI functionality apt for the business.
- ESG Reporting: Every firm is under pressure to perform sustainability tracking. With recent shifts in the global stance on environmental, social, and governance (ESG) reporting, ERP systems include features to adhere to the regulations. ERP consultants must stay informed of the ESG reporting requirements, sustainability metrics, and relevant regulatory practices to help firms stay compliant.
- Soft Skills: Apart from hard-core technology skills, ERP consultants with soft skills like strong communication capabilities effective planning, team collaboration, and team training and mentoring ensure the success of ERP projects. These skills help them easily express, share, and document insights for knowledge sharing, learning, and innovation.
Let’s Align Your ERP Projects with the Right ERP Skills
If you ask us what sets your ERP project plans apart from lofty goals, we will answer with the question, ‘Does your firm have the right ERP skills?’ Throughout Cox-Little’s journey of providing professional IT consulting and ERP staffing services, we have always asked our customers if they have the right know-how. If not, we provide the latest ERP skills and pre-vetted ERP experts to drive tangible outcomes from their ERP projects.
Have you listed the ERP skills your firm needs for 2024 yet? Contact our team guide with expert staffing services for your Q1 ERP goals.





